Capturing Spatial and Temporal Patterns for Facial Landmark Tracking through Adversarial Learning
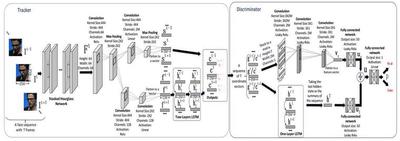
The spatial and temporal patterns inherent in facial feature points are crucial for facial landmark tracking, but have not been thoroughly explored yet. In this paper, we propose a novel deep adversarial framework to explore the shape and temporal dependencies from both appearance level and target label level. The proposed deep adversarial framework consists of a deep landmark tracker and a discriminator. The deep landmark tracker is composed of a stacked Hourglass network as well as a convolutional neural network and a long short-term memory network, and thus implicitly capture spatial and temporal patterns from facial appearance for facial landmark tracking. The discriminator is adopted to distinguish the tracked facial landmarks from ground truth ones. It explicitly models shape and temporal dependencies existing in ground truth facial landmarks through another convolutional neural network and another long short-term memory network. The deep landmark tracker and the discriminator compete with each other. Through adversarial learning, the proposed deep adversarial landmark tracking approach leverages inherent spatial and temporal patterns to facilitate facial landmark tracking from both appearance level and target label level. Experimental results on two benchmark databases demonstrate the superiority of the proposed approach to state-of-the-art work.