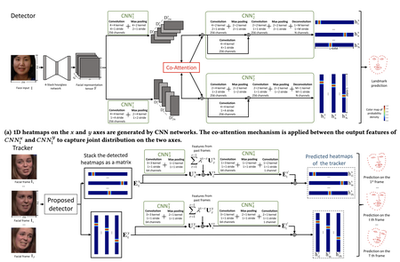
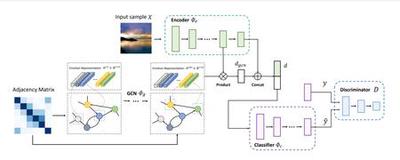
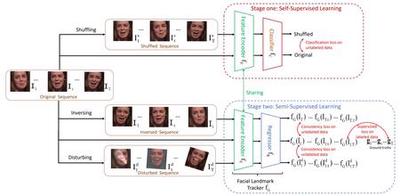
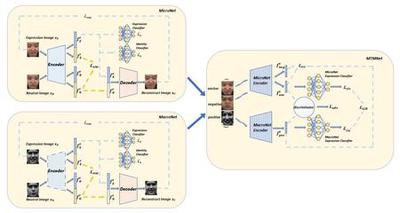
Capturing Spatial and Temporal Patterns for Distinguishing between Posed and Spontaneous Expressions
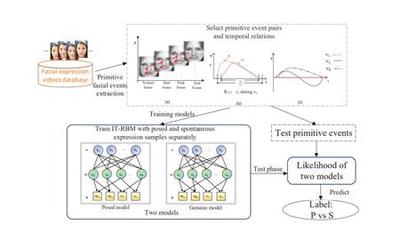
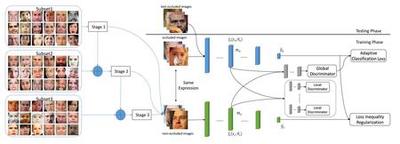
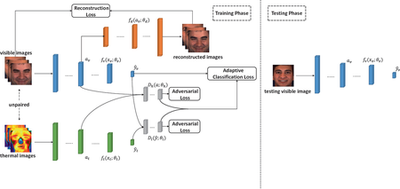
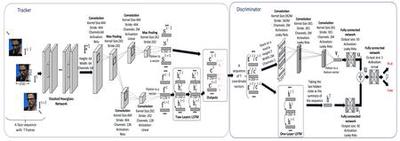
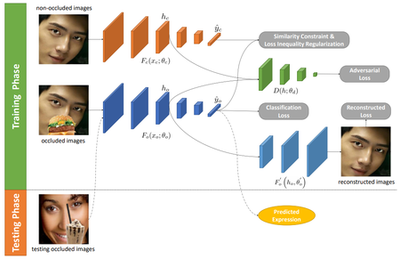
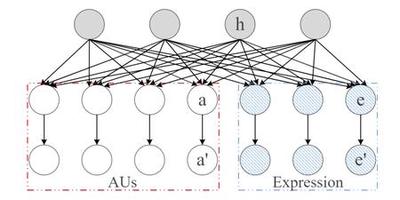
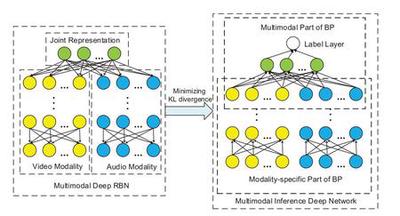
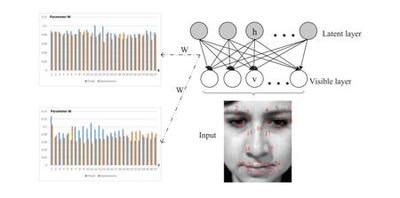
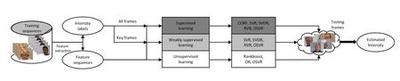
In this paper, we introduce a novel dynamic model, termed as interval temporal restricted Boltzmann machine(IT-RBM), to jointly capture global spatial patterns and complex temporal patterns embedded in posed expressions and spontaneous expressions respectively for distinguishing posed and spontaneous expressions. The proposed IT-RBM is a three-layer hierarchical probabilistic graphical model.