Capturing Spatial and Temporal Patterns for Distinguishing between Posed and Spontaneous Expressions
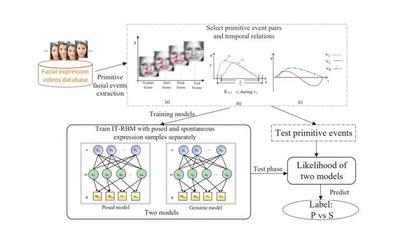
Spatial and temporal patterns inherent in facial behavior carry crucial information for posed and spontaneous expressions distinction, but have not been thoroughly exploited yet. To address this issue, we propose a novel dynamic model, termed as interval temporal restricted Boltzmann machine (IT-RBM), to jointly capture global spatial patterns and complex temporal patterns embedded in posed and spontaneous expressions respectively for distinguishing between posed and spontaneous expressions. Specifically, we consider a facial expression as a complex activity that consists of temporally overlapping or sequential primitive facial events, which are defined as the motion of feature points. We propose using the Allen s Interval Algebra to represent the complex temporal patterns existing in facial events through a two-layer Bayesian network. Furthermore, we propose employing multi-value restricted Boltzmann machine to capture intrinsic global spatial patterns among facial events. Experimental results on three benchmark databases, the UvA-NEMO smile database, the DISFA+ database, and theSPOS database, demonstrate the proposed interval temporal restricted Boltzmann machine can successfully capture the intrinsic spatial-temporal patterns in facial behavior, and thus outperform state-of-the art work of posed and spontaneous expressions distinction.